Biomarker Research
- What is a Biomarker?
Biomarkers are critical to the rational development of medical therapeutics, but significant confusion persists regarding fundamental definitions and concepts involved in their use in research and clinical practice, particularly in the fields of chronic disease and nutrition.
In medicine, a biomarker is a measurable indicator of the severity or presence of some disease state. It is a defined characteristic that is measured as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or responses to an exposure or intervention, including therapeutic interventions.
More generally a biomarker is anything that can be used as an indicator of a particular disease state or some other physiological state of an organism. A biomarker can be a substance that is introduced into an organism as a means to examine organ function or other aspects of health.
- Types and Examples of Biomarkers
Biomarkers are molecules that indicate normal or abnormal process taking place in your body and may be a sign of an underlying condition or disease. Various types of molecules, such as DNA (genes), proteins or hormones, can serve as biomarkers, since they all indicate something about your health. Biomarkers may be produced by the cancer tissue itself or by other cells in the body in response to cancer. They can be found in the blood, stool, urine, tumor tissue, or other tissues or bodily fluids. Notably, biomarkers are not limited to cancer. There are biomarkers for heart disease, multiple sclerosis, and many other diseases.
- Types of Biomarkers: Molecular, histologic, radiographic, and physiologic characteristics.
- Examples of Biomarkers: Blood glucose (molecular) , Tumor size (radiographic), Blood pressure (physiologic).
- Types and Role of Biomarkers in the Clinical Practice
Biomarkers are useful in a number of ways, including measuring the progress of disease, evaluating the most effective therapeutic regimes for a particular cancer type, and establishing long-term susceptibility to cancer or its recurrence. The parameter can be chemical, physical or biological. In molecular terms biomarker is "the subset of markers that might be discovered using genomics, proteomics technologies or imaging technologies. Biomarkers play major roles in medicinal biology. Biomarkers help in early diagnosis, disease prevention, drug target identification, drug response etc.
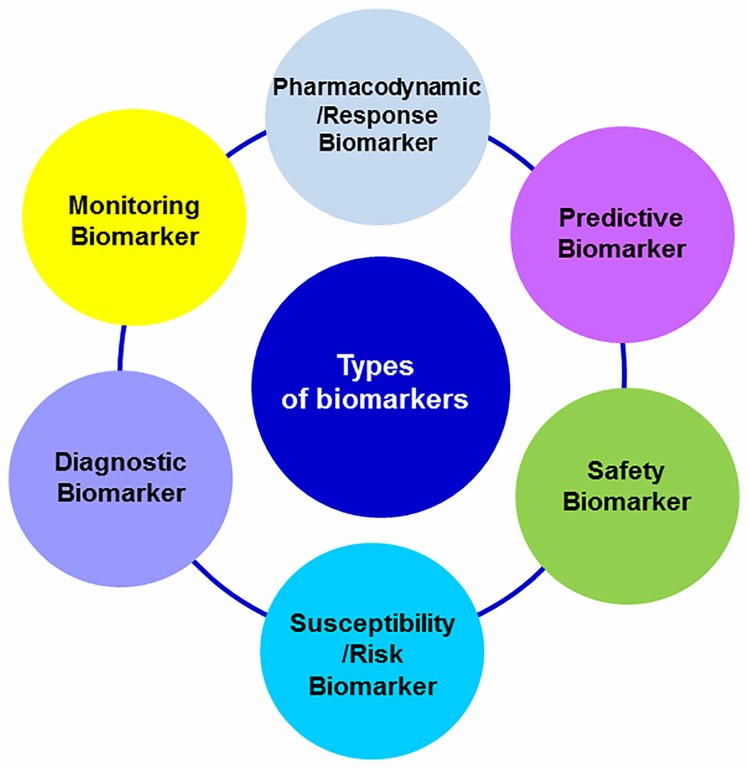
According to their applications, biomarkers can provide complementary information about the disease or the intervention under consideration. Biomarkers may be identified at any event occurring since the pathogenesis, the onset of first clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment outcome or recovery. The FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group distinguished several types of biomarkers based on their main clinical application: diagnostic, monitoring, pharmacodynamic/response, predictive, prognostic, safety, and susceptibility/risk biomarkers (Figure above). A biomarker may meet multiple criteria for different uses or present specific features that enable its particular use.
- Wearable Chemical Sensors for Biomarker Discovery in the Omics Era
Biomarkers are important biological indicators in medical diagnosis and treatment. However, the biomarker discovery and validation process is hampered by the lack of standardized protocols for analytical studies, storage, and sample collection.
Wearable chemical sensors provide a real-time, non-invasive alternative to typical laboratory blood analysis and are an effective tool for exploring novel biomarkers in surrogate body fluids such as sweat, saliva, tears, and interstitial fluid. These devices could enable personalised health monitoring at home remotely and drastically reduce healthcare costs. drug.
[More to come ...]